Page 38 - 21st Century Competencies: Foundation Document for Discussion
P. 38
36 21st Century Competencies
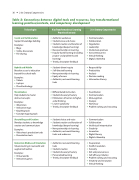
Table 2: Connections between digital tools and resources, key transformational learning practices/contexts, and competency development
Technologies
Key Transformational Learning Practices/Contexts
21st Century Competencies
Social and Collaboration
Support knowledge building
Examples:
• Blogs
• Online discussions • File sharing
• Authentic audiences
• Student voice and choice
• Student creation and iteration of
knowledge (deeper learning)
• New partnerships in learning
• Inquiry-based learning (including
project- and problem-based
learning)
• Timely, descriptive feedback
• Communication • Collaboration
• Negotiation
• Leadership
• Intellectual openness • Conscientiousness
• Critical thinking
• Digital citizenship
Hybrid and Mobile
Broaden access to education beyond the school walls
Examples:
• Tablets
• Laptops
• Cloud technology
• Student-driven inquiry
• Self-directed learning
• New partnerships in learning
• Equity of access
• Authentic, real-world learning
tasks
• Responsibility
• Productivity
• Analysis
• Decision making
• Information literacy
Visualization
Help students to master abstract concepts
Examples:
• 3D printers
• Interactive maps
• Graphing tools
• Concept mapping tools
• Differentiated instruction
• Student discovery/mastery
• Elimination of barriers to higher-
order thinking
• Learner autonomy
• Timely, descriptive feedback
• Coordination
• Communication
• Metacognition
• Analysis
• Numeracy
• Problem solving and reasoning
Storytelling and Creation
Develop students as knowledge creators and communicators
Examples:
• Video/music production tools • Presentation tools
• Student choice and voice
• Student creation and iteration of
knowledge (deeper learning)
• New partnerships in learning
• Authentic, real-world learning
tasks and audiences
• Communication
• Collaboration
• Intellectual interpretation • Creativity
• Innovation
• Digital literacy
• Digital citizenship
Immersive Media and Simulation
Situate learning in real-world and augmented realities
Examples:
• Virtual worlds
• Interactive games
• Authentic, real-world learning tasks
• Student creation
• Student discovery/mastery
• Personalized learning
• Timely, descriptive feedback
• Cooperation
• Conflict resolution
• Curiosity
• Grit and perseverance
• Self-efficacy, initiative
• Problem solving and reasoning • Creativity and innovation
• Critical thinking