Page 219 - Mathematics GRADE 9, DE-STREAMED (MTH1W)
P. 219
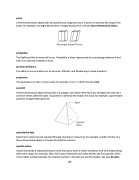
prism
A three-dimensional object with two parallel and congruent faces. A prism is named by the shape of its bases, for example, rectangle-based prism, triangle-based prism. See also three-dimensional object.
probability
The likelihood that an event will occur. Probability is often represented as a percentage between 0 and 100 or as a decimal between 0 and 1.
procedural fluency
The ability to use procedures in an accurate, efficient, and flexible way to solve problems.
proportion
The equivalence of two or more ratios; for example, 3:m:2 = n:8:10. See also ratio.
pyramid
A three-dimensional object whose base is a polygon and whose other faces are triangles that meet at a common vertex called the apex. A pyramid is named by the shape of its base, for example, square-based pyramid, triangle-based pyramid.
quantitative data
Data that is numerical and acquired through counting or measuring; for example, number of sides of a three-dimensional object or amount of rainfall in a season.
quartile values
Values that divide a sequenced data set into four parts, each of which represents 25% of the data falling within that range. For example, 25% of the data is below the point that defines the first quartile, which is the middle number between the smallest number in the data set and the median. See also box plot.
218